Beacon Machine Manufacturing Co.,ltd
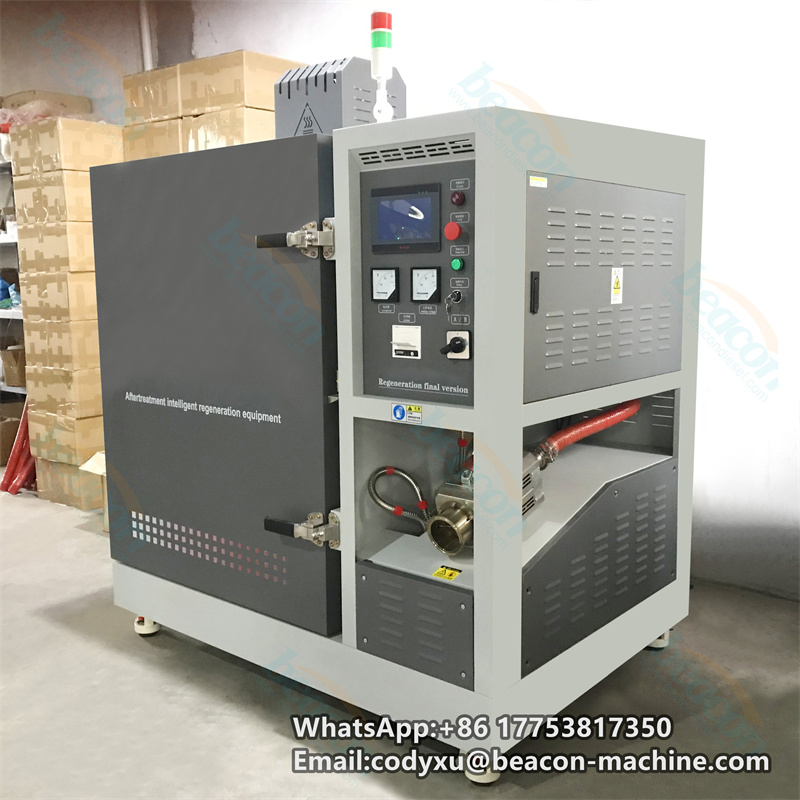
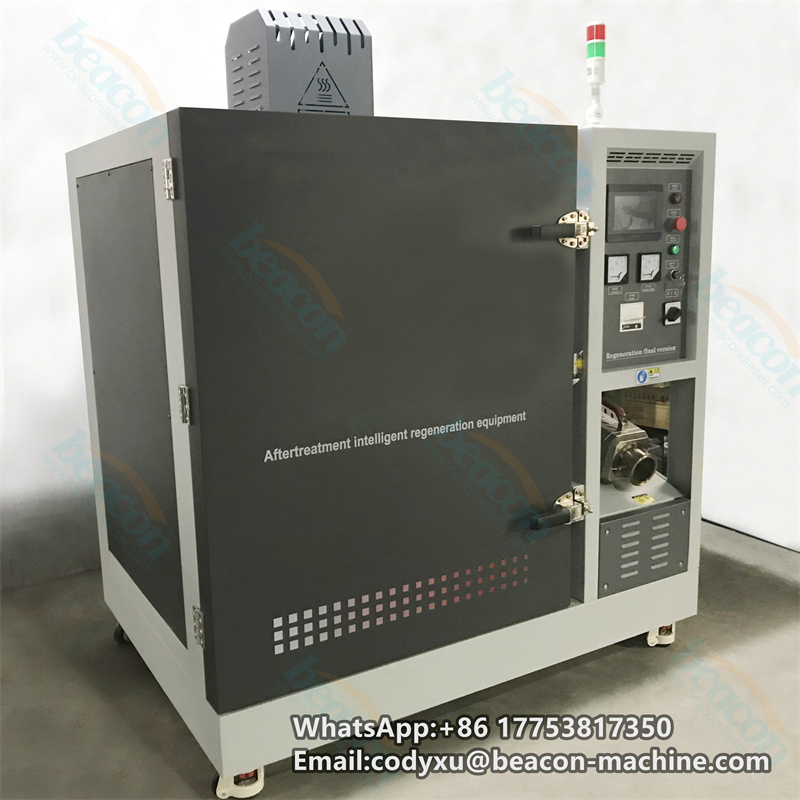
DPF-RGE Regenerator Filter Diesel Particulate Cleaning Machine Intelligent Post-processing Regeneration Equipment
DPF-RGE Regenerator Filter Diesel Particulate Cleaning Machine Intelligent Post-processing Regeneration Equipment
Introduction
Introduction
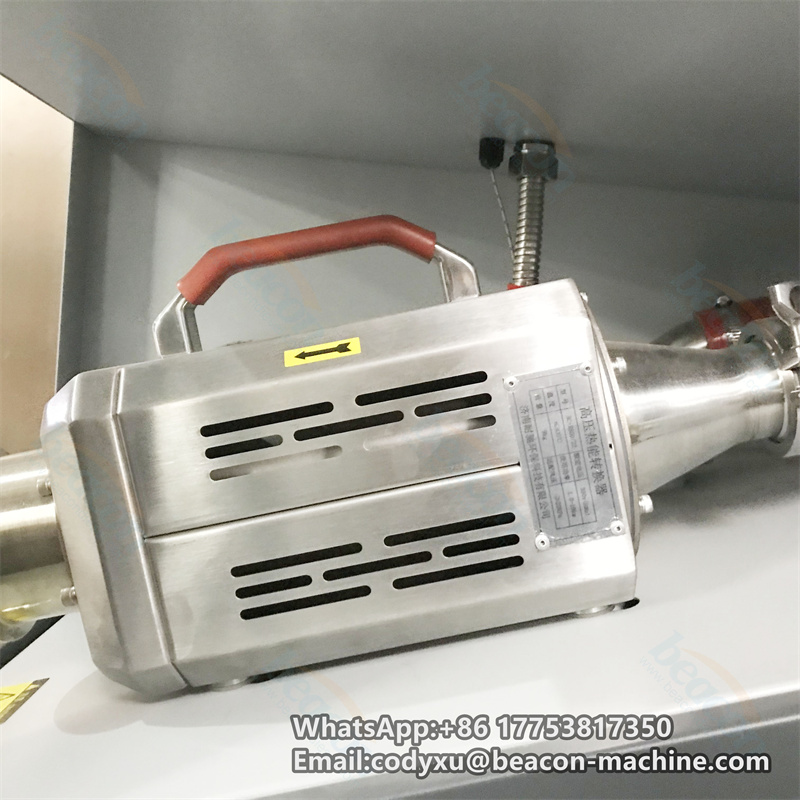
The full English name of DPF is "Diesel Particulate Filter", which literally translates to "diesel particulate filter", also called diesel particulate capture regenerator. It is a device that can reduce the emission of particulate matter (PM) in the exhaust. During the working process of the trap, particles will accumulate in the filter. When it reaches a certain value, it will cause the engine's power and economic performance to decline. The deposited particles must be removed in time to ensure that the DPF continues to work normally. It is the so-called DPF regeneration.
DPF is also called wall-flow particle trap. Its core function is that after engine exhaust passes through DPF, gaseous pollutants can flow out through the pore wall, and particles are trapped inside the DPF by the pore wall. Then, under certain conditions, the carbon (C) particles are converted into gaseous substances and discharged.
The core of the diesel engine exhaust carbon particles (soot) collected in the DPF is solid carbon (C), and the outside contains polymers produced by incomplete engine combustion. In layman's terms, its role is to collect the carbon particles in the exhaust first, and then concentrate them to a certain extent, to convert exhaust pollutants into non-polluting gases.
The full English name of DPF is "Diesel Particulate Filter", which literally translates to "diesel particulate filter", also called diesel particulate capture regenerator. It is a device that can reduce the emission of particulate matter (PM) in the exhaust. During the working process of the trap, particles will accumulate in the filter. When it reaches a certain value, it will cause the engine's power and economic performance to decline. The deposited particles must be removed in time to ensure that the DPF continues to work normally. It is the so-called DPF regeneration.
DPF is also called wall-flow particle trap. Its core function is that after engine exhaust passes through DPF, gaseous pollutants can flow out through the pore wall, and particles are trapped inside the DPF by the pore wall. Then, under certain conditions, the carbon (C) particles are converted into gaseous substances and discharged.
The core of the diesel engine exhaust carbon particles (soot) collected in the DPF is solid carbon (C), and the outside contains polymers produced by incomplete engine combustion. In layman's terms, its role is to collect the carbon particles in the exhaust first, and then concentrate them to a certain extent, to convert exhaust pollutants into non-polluting gases.
parameter
Model: DPF - RGE
Operating temperature; 0-800 degrees
Total power: 20KW
Maximum wind pressure: 23KPa
Rated voltage: 380v (50HZ)
Equipment total size: 1180 * 630 * 1120 (mm)
Weight: 500kg
*Test data from Beacon laboratory
Operating temperature; 0-800 degrees
Total power: 20KW
Maximum wind pressure: 23KPa
Rated voltage: 380v (50HZ)
Equipment total size: 1180 * 630 * 1120 (mm)
Weight: 500kg
*Test data from Beacon laboratory
Related products